Building a Stock Screener in Python- Part 1
In this post, I’ll share how to create a stock screener — a program which can filter stocks based on user preferences — from scratch (and for free) using python. This project will be broken into 3 parts-
- Scraping data
- Storing data
- Screening data
Before we dive into programming, let’s start by asking why anyone would want to build a stock screener.
Why
Let’s think about personal finance and investments for a second: why would someone strategically pick healthy stocks which provide a high return-on-investment while maintaining relatively low levels of risk?
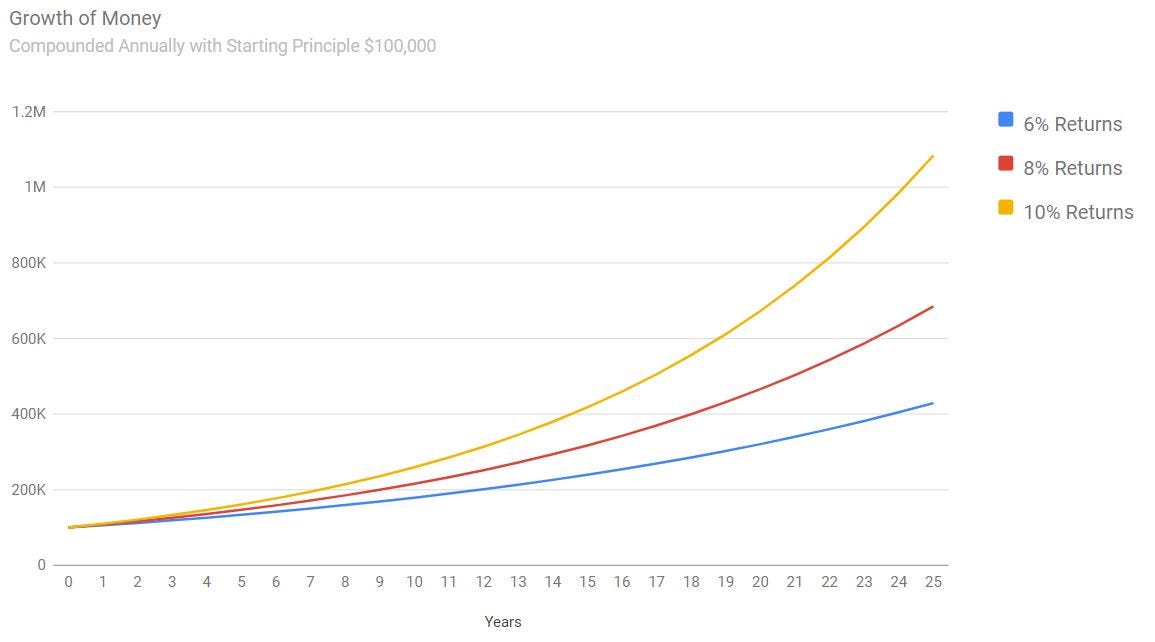
Difference between growing your money at 6%, 8% and 10%
Because your choice of stocks directly impacts your portfolio’s returns and can be the difference between becoming a Millionaire at age 35 vs 55. Even a few bad stocks in your portfolio can greatly decrease performance, so it’s important to carefully analyze and filter companies.
How
So now that you know why, let’s talk about how someone could strategically pick healthy stocks which provide a high return-on-investment while maintaining relatively low levels of risk? There’s a few methods out there for people wondering, but one of the most common analysis strategies for picking companies is Technical Analysis.
Technical Analysis is a method by which analysts use data to find patterns and trends to generate predictions about company performance. The key word in the previous statement is data. Sources like Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Market Watch etc. act like central hubs for stock data. They collect, visualize and share this information with the rest of the world. Investors use these websites to analyse companies and pick the ones they see fit; thus the terminology, filtering. While individually looking through hundreds of web-pages and picking companies is a perfectly acceptable method of building a portfolio, computer scientists know better. This is a where a stock screener comes into play.
Stock Screeners
A stock screener is a program which can filter stocks based on certain criteria. It can be used to analyze a large volume of companies in a relatively short period of time. Keep in mind that a stock screener is not a program that can (or should) replace religious analysis of a company’s performance before any personal investment decision is made, but rather is a way to effectively decrease the number of companies which need to be analyzed. A trivial, but important example is shown below-
Without any filter
Approximately 13,547 companies are listed on Yahoo Finance. This is a huge number of companies to filter through for individual examination

Screen without any filters
With a basic filter
Even a basic screen (companies which have seen a percent change in price greater than 10%, thus have a highly positive price change) decreases the number of companies by over 90%, making individual examination a possibility.

Screen with a basic filter
With a selective filter
The following filter is fairly selective: it is only looking at Mega Cap companies (Market Cap over $100B), with a current ratio greater than 1 (indicating good liquidity health), and an expected PEG ratio greater than 2 (indicating very good expected growth over 5 years). The list of companies is down to 9, which is a very manageable number to individually inspect.
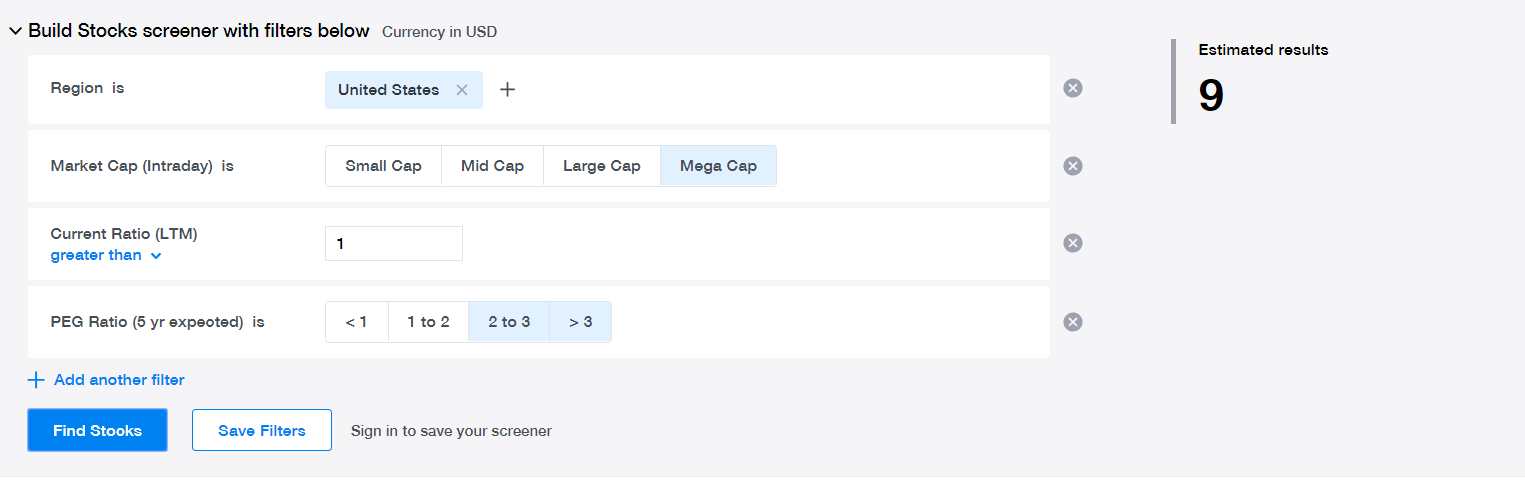
Screen with a fairly selective filter
By now I’m sure you understand the importance of having a stock screener and hope you’re excited to build one from scratch! While there are a few paid and free stock screeners available online, building one from scratch enables you to really customize your screens, implement more complicated/personalized methods and take your filtering abilities to the next level. Now let’s get down to business.
Part 1: Scraping Data
Part 1, and arguably the most important part of building a stock screener, is the ability to get your hands on the data. There are many stock data API’s available out there, but do not be fooled, most of them are fairly expensive or limit the number of requests, making them severely infeasible for a stock screener. That is why I will show you how to scrape stock information in this part. You can use the framework discussed below on different websites/data based on your needs.
The following are the main steps taken to scrape the data.
- Find a reliable source
- Determine data to be scraped
- Create scraping methodology
- Build algorithm
Find a reliable source
This is a website that publishes the stock information that you’re trying to scrape. Be sure to check the website’s terms and conditions regarding data scraping to avoid unnecessary problems. In this case, I’m collecting the data for educational and research purposes only, and do not wish to sell this information elsewhere. I decided to use Yahoo Finance, as it is a very reliable source of data. Additionally, they also keep their information well organized as we’ll discuss below.
Determine Data to be scraped
This step is very important, as it constraints the data that the scraper will be collecting. In order to do this, we’ll be taking a look at the typical Yahoo Finance page of a company and decide what data is relevant to us. Here’s what the main Yahoo page of Apple Inc. looks like (as of December 30, 2018):
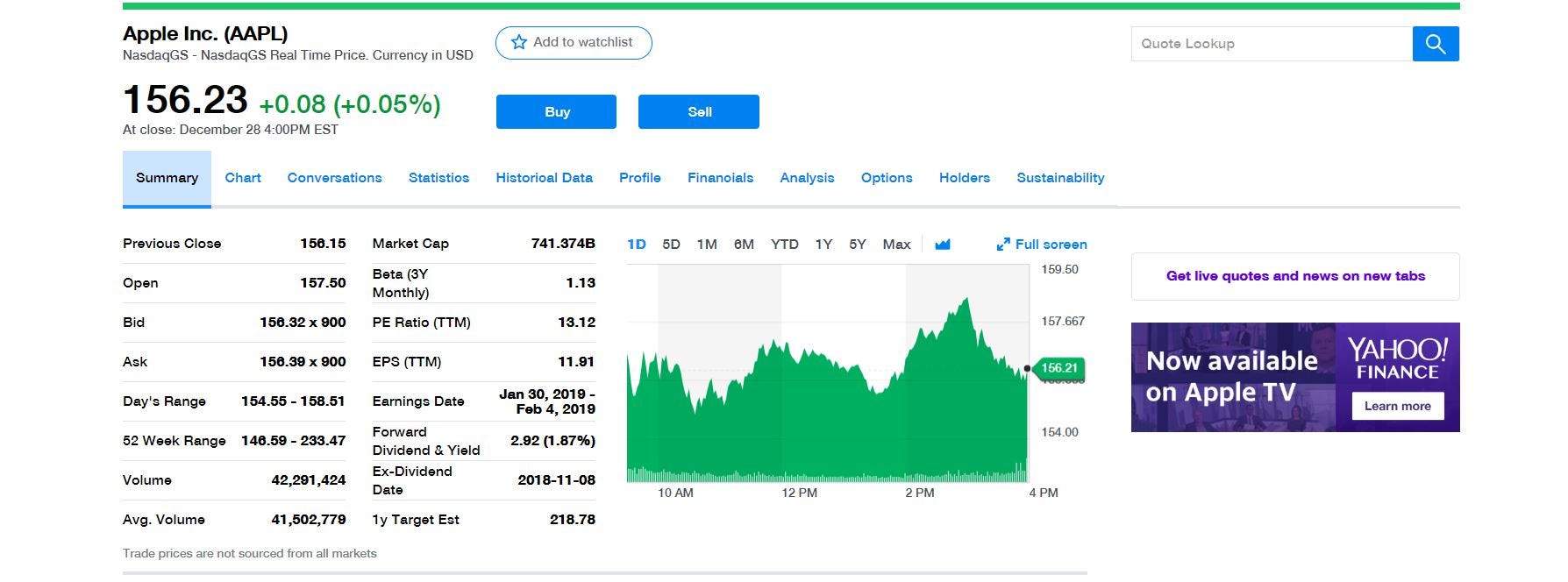
Yahoo Finance page for Apple Inc. (AAPL)
While the summary tab contains some very useful information about this stock, we’re interested in indicators which tell us more about the health of this company. For this, we’ll turn to the statistics tab, which looks like so-
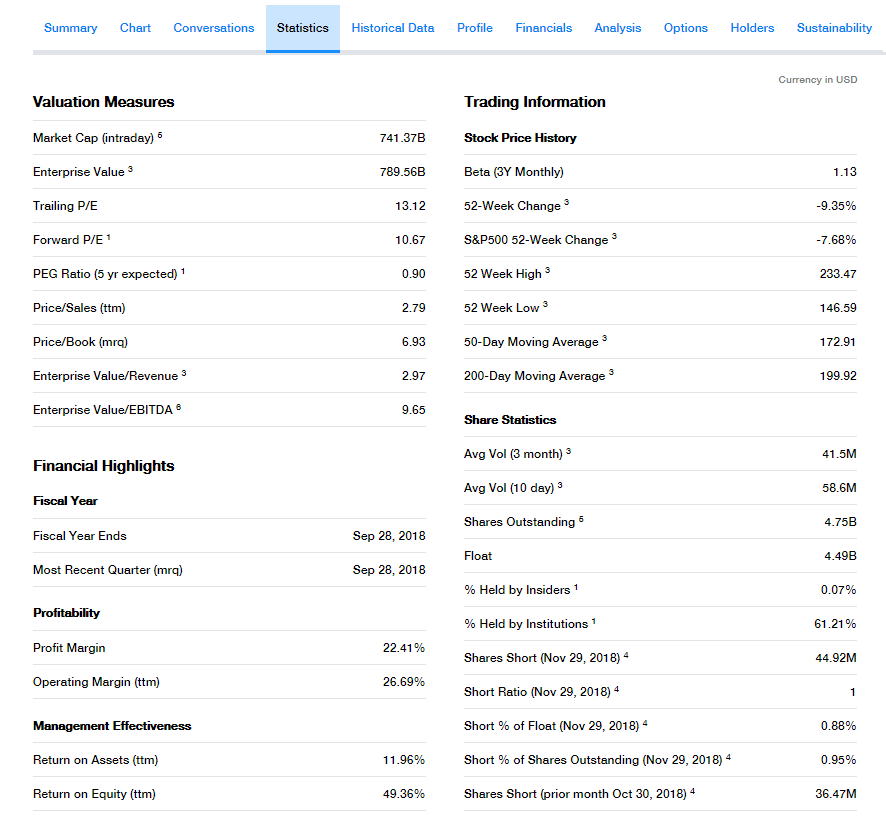
Statistics page of Yahoo Finance for Apple Inc. (AAPL)
As you can see, this page contains a myriad of data and is neatly arranged into tables, making it perfect for our program. We note the URL (which is shown below) and move on to the scraping methodology. You can check out the web page for Apple yourself using the link too.
http://finance.yahoo.com/q/ks?s=aapl
Create Scraping Methodology
Before we can talk about the scraping methodology, you need to understand Beautiful Soup. If you already know the basics feel free to move on, but if you need a refresher, check out this article.
The scraping methodology refers to the method by which beautiful soup finds the relevant <div>'s <table>'s etc. inside the web page’s HTML source code. This is usually achieved by inspecting the different elements (right click -> inspect element) inside a web page, till you can find a consistent class, attribute etc. which captures all the data you want. Here’s some photos of me inspecting elements in the Yahoo Finance pages to further show this point.
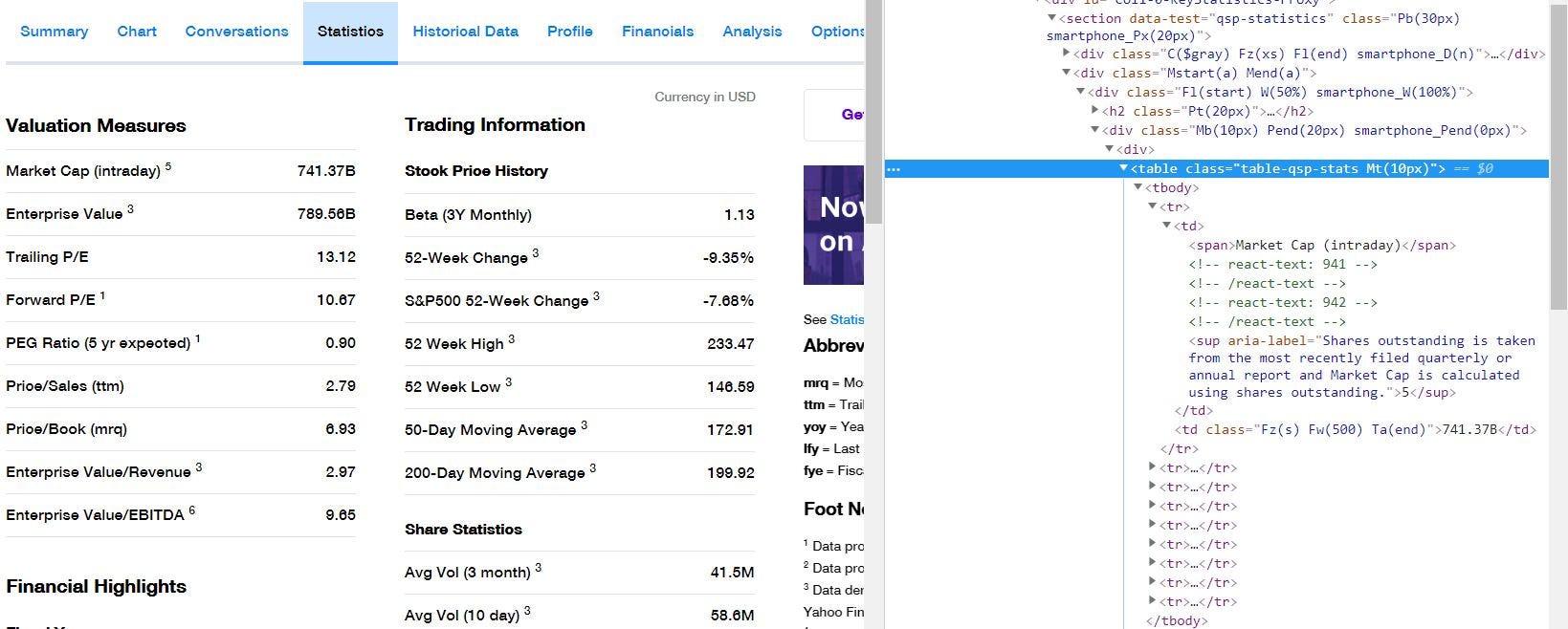
Inspecting elements on the Yahoo Finance web page for Apple Inc. (AAPL)
As you can (barely) tell from the above photo, each of the name-value pairs, like Market Cap (intraday), 741.37B are displayed using <span> and <td> tags inside the same <tr> tag. Further, all of these <tr> are within the same <table> tag with a special class: table-qsp-stats. This class gives us a way to distinguish the data-tables from all other elements on the web page. On further inspection, you can also see that the class is attached to every table tag that contains relevant data.
This is perfect for us, as we can easily use Beautiful Soup to navigate to the table (which contains our special class name), iterate through the rows and capture relevant information. Now, we can start coding this algorithm.
Build Algorithm
Now we start with our actual python program. Here’s our algorithm, laid out step-by-step-
- Create URL for given stock
- Extract HTML from web page
- Find all tables that contain class
table-qsp-stats - For each table, iterate through rows
- For each row store
<span>text as key and<td>text as corresponding value in dictionary
Here’s the syntax of the function, which accepts a stock symbol (for reference):
def scrape_yahoo(stock):
Now building on this, we need to create the URL (using the stock symbol) and extract the HTML from the web page using urllib2 and Beautiful Soup-
url = ('http://finance.yahoo.com/q/ks?s=' + stock)
page = urllib2.urlopen(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(page, 'html.parser')
Now we move on to finding the relevant tables and processing each of the rows.
Note: technicals is an empty dictionary initialized earlier.
tables = soup.findAll('table', {"class" : 'table-qsp-stats'}) for table in tables:
table_body = table.find('tbody')
rows = table_body.find_all('tr') for row in rows:
# span tags contain the indicator name
col_name = row.find_all('span')
col_name = [cell.text.strip() for cell in col_name]
# td tags contain the indicator values
col_val = row.find_all('td')
col_val = [cell.text.strip() for cell in col_val]
technicals[col_name[0]] = col_val[1]
The full code for this data scraper can be found on this github repository.
Wrap up and what next?
So now you have it! A way to scrape stock data off of Yahoo Finance for use in your very own stock screener. If you want to continue on in this series, feel free to check out Part 2. In part 2 we build upon this algorithm to store the data collected and then we’ll be ready to create filtering queries to wrap up the stock screener.
If you have any questions, feedback or comments, feel free to get in touch with me through LinkedIn, or my website.